What Is The Proton Gradient In Cellular Respiration
Olivia Luz
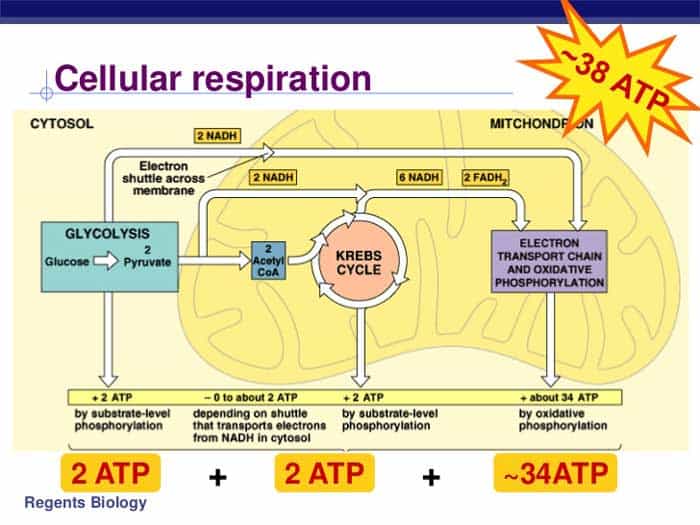
This electrochemical gradient formed by the accumulation of h also known as a proton on one side of the membrane compared with the other is referred to as the proton motive force pmf.
Production of h2o 4. A higher concentration of protons on one side of a membrane than the other although the path of one glucose molecule through glycolysis generates a total of four atp molecules there is a net gain of only two atp for each glucose molecule that enters the pathway. A difference in the concentration of protons h on either side of a membrane. Two protons reduce quinone to quinol and four protons are released from two ubiquinol molecules.
These gradients together store potential energy in the cell which is available for work. Electrons moving through the electron transport chain. What is the proton gradient in cellular respiration. The movement of protons h across a selectively permeable semipermeable membrane c.
The overall reaction is broken into many smaller ones when it occurs in the body. Chemically cellular respiration is considered an exothermic redox reaction. Overview of cellular respiration. During aerobic cellular respiration a proton gradient in mitochondria will be generated by and used primarily for.
RELATED ARTICLE :
- what is the largest forest in the world
- what is the legend of seven spanish angels
- what is the lcm of 10 and 12
A proton gradient is formed by two quinol 4h 4e oxidations at the qo site to form one quinol 2h 2e at the qi site in total six protons are translocated. One common mechanism for doing this is a proton pump which moves hydrogen ions to one side of the membrane creating a proton gradient or membrane potential. A difference in atp concentration across the mitochondrial membrane b. Cells often actively transport ions across membranes creating membrane potential just for this purpose.
Glucose breaking down in glycolysis. What is the proton gradient in cellular respiration. The electrochemical proton gradient the electrochemical proton gradient is a difference hydrogen ion concentration across a membrane producing a concentration gradient and an electrical potential gradient.
Source : pinterest.com


















