What Is The Main Idea Of Operant Conditioning
Olivia Luz

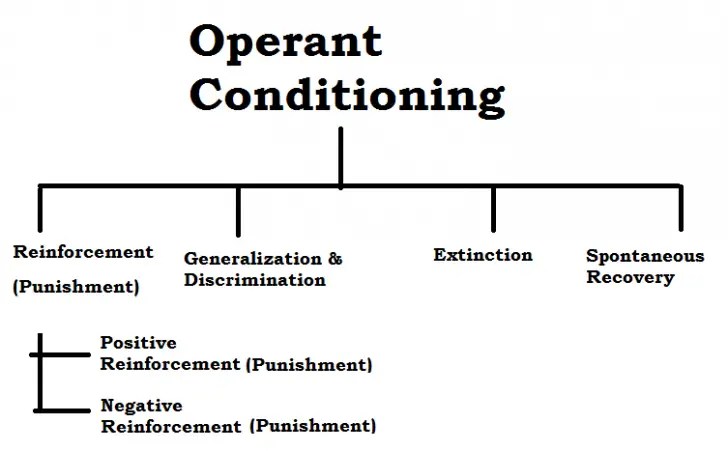
In operant conditioning behaviors are strengthened or weakened based on the consequences of that behavior.
Skinner based his theory in the simple fact that the study of observable behavior is much simpler than trying to study internal mental events. It is unethical for a researcher to induce fear in a child since it is harmful to induce fear. Through operant conditioning an individual makes an association between a particular behavior and a consequence skinner 1938. Operant conditioning or instrumental conditioning focuses on using either reinforcement or punishment to increase or decrease a behavior.
The study of operant conditioning helps to understand relations between a behavior and the consequence it offers. Operant conditioning also called instrumental conditioning is a type of associative learning process through which the strength of a behavior is modified by reinforcement or punishment it is also a procedure that is used to bring about such learning. By the 1920s john b. Through this process an association is formed between the behavior and the consequences of that behavior.
Watson had left academic psychology and. Operant conditioning sometimes referred to as instrumental conditioning is a method of learning that occurs through rewards and punishments for behavior. Operant conditioning is the process of learning through reinforcement and punishment. Through operant conditioning an association is made between a behavior and a consequence whether negative or positive for that behavior.
RELATED ARTICLE :
- what is the name of harry potters owl
- what is the next dog man book called
- what is the official first day of summer
Operant conditioning can be defined as a form of learning in which behaviors are dependent on or controlled by its rewards and consequences. In classical conditioning a previously neutral stimulus that after association with an unconditioned stimulus us comes to trigger a conditioned response shaping an operant conditioning procedure in which reinforcers guide behavior toward closer and closer approximations of the desired behavior.
Source : pinterest.com